- Treatments
- Laparoscopy Gynae Surgery
- Ovarian Cyst Removal
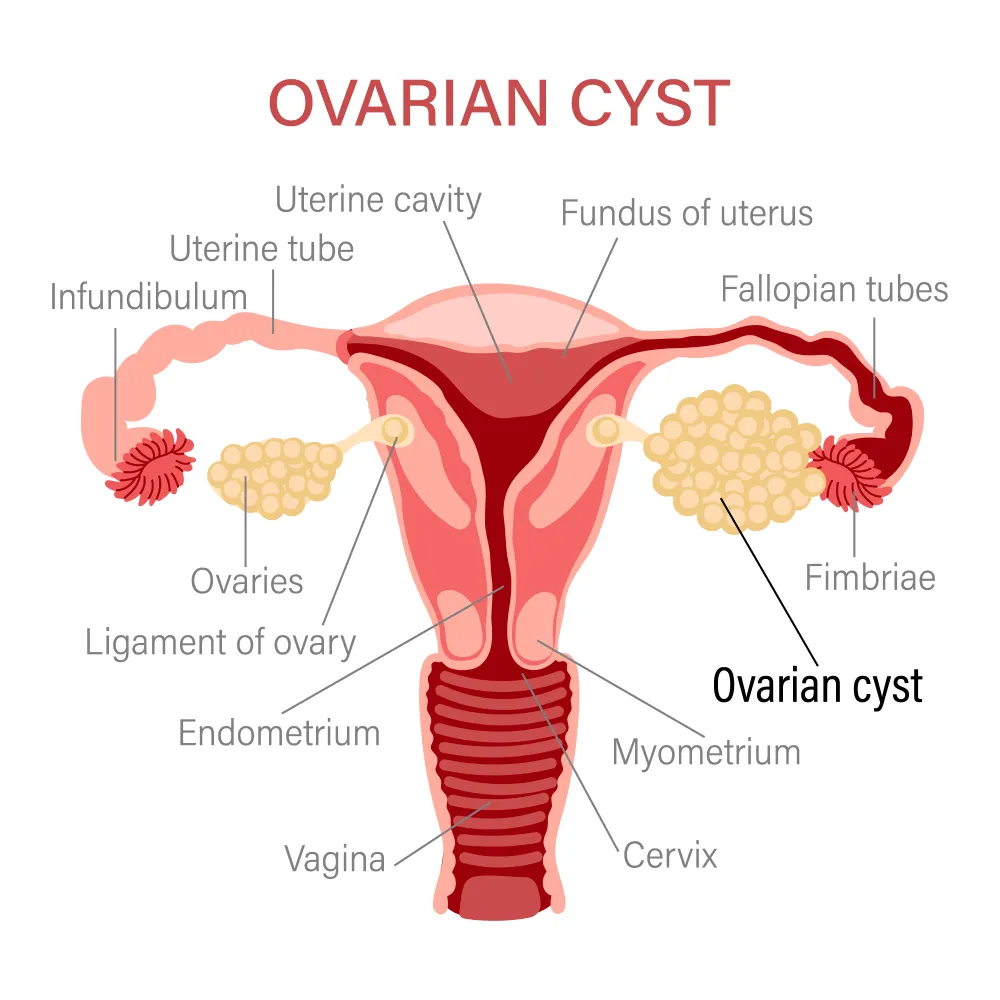
Ovarian Cysts
Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled or semisolid sacs that can develop on or within one or both ovaries. These cysts are relatively common and often occur as a part of the normal menstrual cycle.
Types of Ovarian Cysts
Functional Cysts Functional cysts are the most common type of ovarian cysts and are not associated with any disease. They typically develop as a result of ovulation, which is the release of an egg from the ovary.
Other Types of Cysts Not all ovarian cysts are linked to the menstrual cycle. While they are not always harmful, your healthcare provider may monitor these cysts to prevent complications. These include:
- Cystadenomas: These cysts develop on the surface of the ovary and may contain either thin, watery fluid or thicker, mucous-like material.
- Dermoid Cysts (Teratomas): Dermoid cysts are made up of different types of tissues, including skin, hair, teeth, and sometimes even brain tissue.
- Endometriomas: These cysts are filled with endometrial tissue, the same tissue that lines the uterus and sheds during menstruation.
- Ovarian Cancer Cysts: Unlike the other types, ovarian cancer cysts (tumors) are solid masses made up of cancerous cells.
Who Can Develop Ovarian Cysts?
Anyone with ovaries can develop ovarian cysts, though the likelihood increases based on several factors:
- Age: Ovarian cysts are more common in individuals who have not yet gone through menopause.
- Pregnancy: Cysts are more likely to form and persist during pregnancy.
- History of Ovarian Cysts: A history of ovarian cysts increases the chances of developing another.
- Current Medical Conditions: Conditions like endometriosis or hormonal imbalances can increase the risk of ovarian cysts.
What Causes of Ovarian Cysts?
- Abnormal Cell Reproduction: This can lead to the formation of cysts like dermoids and cystadenomas.
- Endometriosis: Advanced endometriosis can cause cysts to form on the ovary.
- Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID): Severe infections in the pelvis can spread to the ovaries, resulting in cysts.
Symptoms of Ovarian Cysts Small cysts often go unnoticed as they may not cause symptoms. However, larger cysts can lead to:
- Pelvic pain or a dull ache in the lower back.
- A feeling of fullness or bloating in the lower abdomen, often more pronounced on one side.
- Pain during intercourse.
- Painful periods.
Persistent symptoms may indicate polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), a condition that causes irregular periods, obesity, infertility, and other hormone-related issues, including hirsutism (excessive body hair growth) and difficulty losing weight.
Complications of Ovarian Cysts
- Cancerous Cysts: Post-menopausal ovarian cysts have a higher likelihood of being cancerous.
- Ruptured Cysts: While many functional cysts rupture without symptoms, some can cause severe pain and abdominal swelling if they break.
- Ovarian Torsion: Large cysts can cause the ovary to twist, cutting off blood supply and leading to severe pain, nausea, and vomiting. This condition requires immediate medical attention.
Diagnosing Ovarian Cysts
- Pelvic Exam: To check for lumps or changes in the pelvis.
- Ultrasound: This imaging technique uses sound waves to detect cysts, determine their location, and whether they contain fluid or solid material.
Laparoscopy Ovarian Cyst Removal
Laparoscopy is the most common method for removing ovarian cysts, especially if they are small and non-cancerous. During this procedure, a small camera (laparoscope) is inserted through a small incision in the abdomen. The surgeon uses specialized instruments to remove the cyst through these tiny incisions.
Post-Surgery Care
- Monitoring: Follow-up appointments are important to monitor healing and to ensure that no new cysts are forming.
- Activity: Patients are generally advised to avoid heavy lifting, strenuous activity, and intercourse until fully healed, as directed by their healthcare provider.
- Pain Management: Pain after surgery is usually managed with over-the-counter pain relievers or prescribed medication if needed.
When to Contact Your Doctor
Reach out to your doctor immediately if you experience any of the following after surgery:
- Intense pain or swelling in the abdomen.
- Fever or signs of infection around the incision site.
- Heavy vaginal bleeding.
- Trouble urinating or having bowel movements.
Ovarian cyst removal is a common procedure that can relieve symptoms and prevent complications. If you have concerns about ovarian cysts, discuss them with your healthcare provider to determine the best course of action.